Licensing Model Migration Plan
Summary
Organizations can now deploy Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) without Azure Arc. This option is perfect for customers with mixed and hybrid server environments who want to consolidate protection under the Defender for Servers licensing model. The new “arc-less” capability is a tenant-level setting that automatically switches the licensing model from a billable SKU (Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for Server) to consumption in Azure using Defender for Cloud (either P1 or P2), without additional agent deployments. This means that we can deploy Defender for Endpoint from the Microsoft 365 Defender portal using the onboarding package or script, with billing and licensing being managed through Azure/Defender for Server, and without the need for additional agents, extensions, or products.
Direct onboarding integrates Defender for Endpoint with Defender for Cloud without additional software on your servers. Once enabled, it displays non-Azure server devices in Defender for Cloud under a designated Azure Subscription (for licensing, billing, alerts, and security insights) and in the Microsoft Defender Portal. Note that this “arc-less” mechanism does not include server management capabilities like Azure Policy or Guest configuration. For those additional features, the use of Azure Arc agent is required.
Switching from Direct onboarding to Azure Arc incurs no additional cost (Unless changing from P1 to P2). If you need to collect logs via AMA or use other unsupported features, you can install the Azure Arc agent without offboarding from Defender for Endpoint.
Simplified step-by-step guidance to Transitioning from MDE SKU to Defender for Server P1/P2
- Create a new subscription or identify which current subscription will be used for MDE integration.
- Enable Defender for Server P1/P2 licenses in the selected subscription
- Enabled Direct Onboarding in the subscription
- If Defenders for Servers is off for this subscription when Direct Onboarding is Enabled – Defenders for Servers P1 will be enabled for it automatically
- Continue onboarding the server to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint using the onboarding script via GPO or SCCM or the current onboarding mechanisms.
- All server will be automatically added into the designated subscription only for licensing applications.
How to Enable Defender for Server with Direct Onboarding and a Designated Subscription
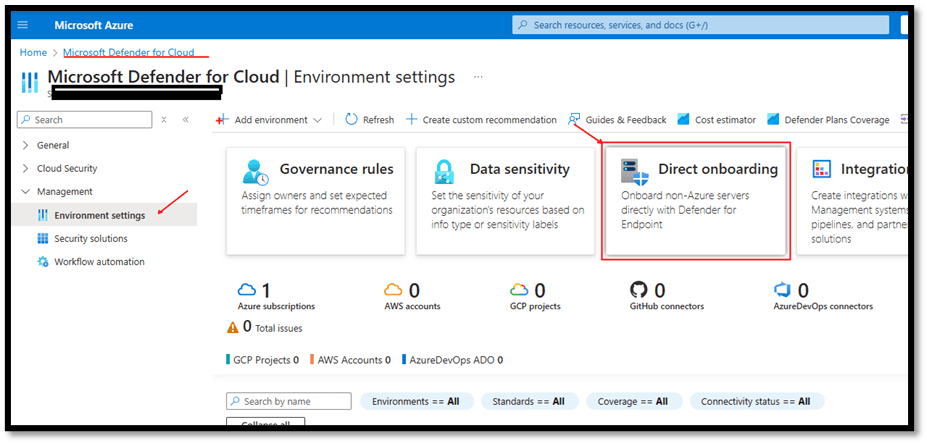
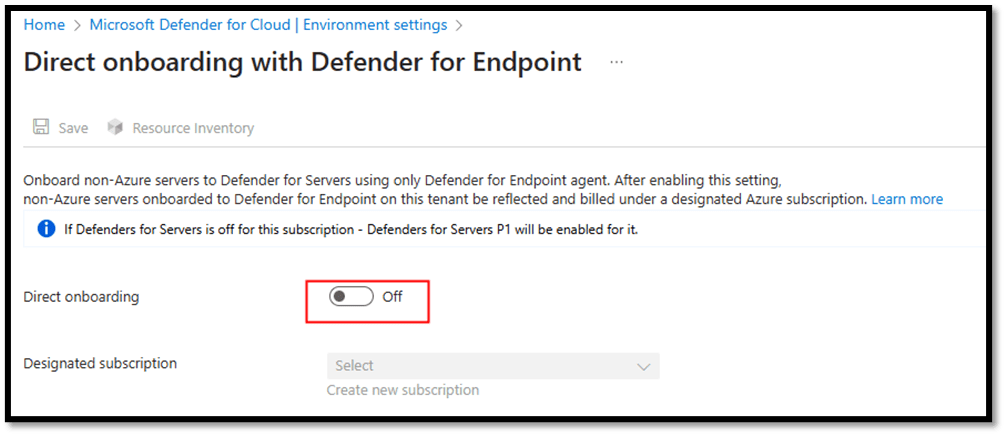
- Go to Defender for Cloud > Environment Settings > Direct onboarding.
- Switch the Direct onboarding toggle to On.
- Select the subscription you would like to use for servers onboard directly with Defender for Endpoint.
- Select Save.